HOOK BLOCK FOR CRANES
HOOK BLOCK FOR CRANES
The manufacturing of Hook Block is a complex process involving material selection, manufacturing process, heat treatment, inspection and other steps. The following are the main steps and key points of crane hook manufacturing:
1. Material Selection:
The material of hook block is usually selected from high-strength, wear-resistant and fatigue-resistant alloy structural steel. Commonly used materials include 20 high-quality carbon steel or hook-specific materials DG20Mn, DG34CrMo, etc.
The material should have high mechanical strength and good impact toughness to withstand the impact load at the moment of starting and stopping the lifting mechanism.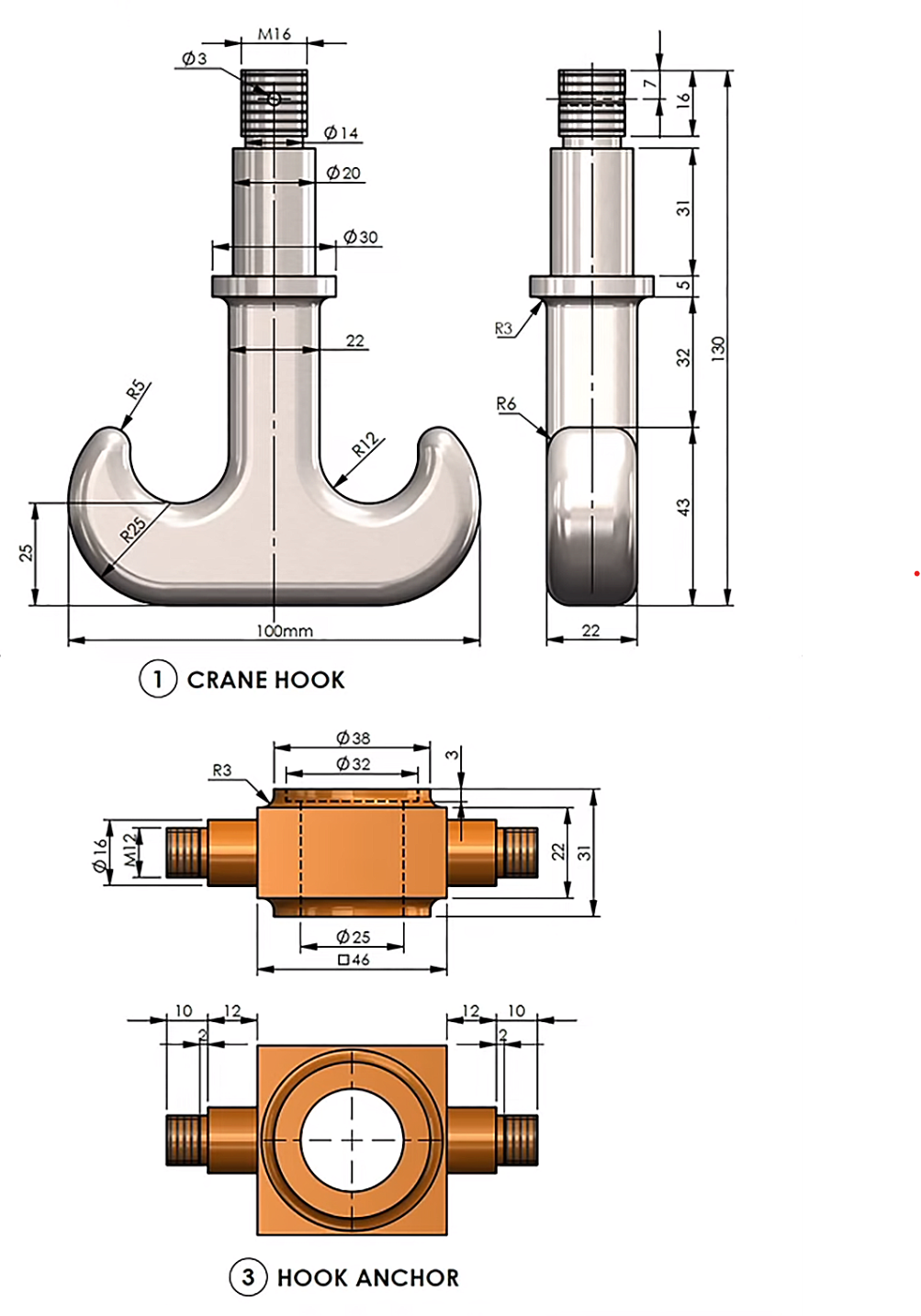
2. Manufacturing Method
The hook block is divided into forged hooks and laminated hooks according to the manufacturing method. Forged hooks are manufactured as a whole, simple to manufacture, easy to use, and suitable for work occasions with a lifting weight of less than 80 tons. Laminated hooks are made of riveted steel plates cut and formed from several pieces. They are safer, but have a larger dead weight and are suitable for cranes with large lifting weights or lifting molten steel buckets.
The manufacturing process of forged hook block includes placing pre-heated steel billets into a forging machine and forming them into the initial shape of the hook by impact or extrusion. During the forging process, attention should be paid to controlling the temperature, force and speed to ensure the strength and shape of the hook.
3. Heat Treatment
In order to eliminate cold stress, thermal stress and welding stress, the hook must be properly heat treated during the manufacturing process, such as tempering.
4. Inspection and Marking
The purchased hook block should be used only with the manufacturer’s certificate and other technical documents. Important departments such as railways and ports purchase hooks, and the hooks must be strictly inspected (defect detection) before leaving the factory.
The surface of the hook block should be smooth and must not have defects such as cracks, folds, sharp angles, burrs, peeling, overburning, etc.
The shortest distance of the hook opening should be printed or inlaid with a mark that is not easy to wear, and the distance between the marks should be measured as a basis for detecting whether the opening degree changes during use.
5. Safety Requirements:
The hook must not have defects that affect the safe use performance; hook defects must not be welded.
The hook should be able to reliably support 2 times the test load.
6. Scrap Standards
The hook block should be scrapped if there are cracks, dangerous sections are worn or corroded, the hook handle is plastically deformed, or the opening increases by more than the specified proportion compared to the original size.
The above steps and key points are summarized based on national standards and industry practices to ensure the manufacturing quality and safety performance of crane hook block.